Linline In Surgery
Ulcers & Wound healing
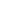
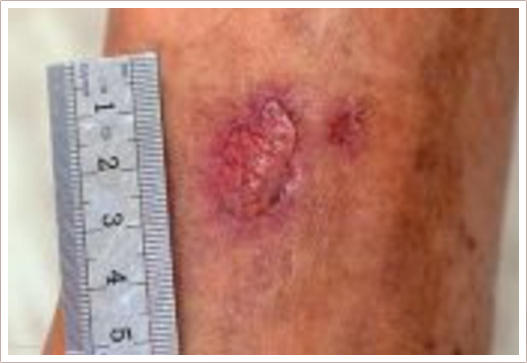
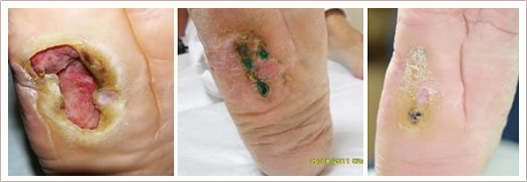
A chronic or non-healing wound or ulcer is one that does not heal in six to eight weeks with traditional wound care. Such wounds can cause tremendous suffering as well as serious infections, illness or loss of a limb.
There are many different types of chronic ulcers and wounds: pressure ulcers (bed sores), venous ulcers, arterial ulcers, diabetic foot and leg ulcers, wounds caused by radiation therapy, purulent wounds, non-closing surgical wounds etc. Trophic ulcers are a complex of symptoms caused by impaired trophism of tissues (due to inadequate blood inflow or blood outflow, impaired nervous regulation or a host of other causes or their combinations).
Chronic ulcers and wounds persist despite appropriate care due to many reasons, but the most common cause is wound infection. Antibiotics, whether topical, oral or intravenous, may be given to eradicate any bacterial infection and promote healing. Despite using antibiotics hospital-acquired infections (HAI) represent one of the major problems in health care delivery due to the growing resistance of wound micro flora to most antibiotics. According to World Health Organisation hundreds of millions of patients are affected by HAI worldwide each year, leading to significant mortality and financial losses for health systems.
Our Solutions
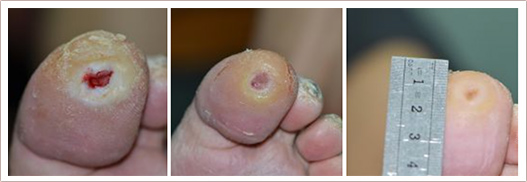
RecoSMA is the new unique method for chronic ulcer and wound healing, developed and patented by LINLINE. It stimulates regenerative processes in the ulcerated tissue and improves trophism in the surrounding which leads to a decrease in the size of ulcers and up to the complete defect closure.
The new RecoSMA technology is well-established for treatment of chronic, non-healing ulcers and wounds based on the new approach with Er:YAG laser associated with the unique SMA module (Spatially Modulated Ablation).The treatment is carried out in 3 stages:
- Wound cleaning: removal of dry tissue composed of keratin layers and/or dead cells and debris using Er:YAG laser radiation with a wavelength of 2940 nm.
- Wound disinfection: bacterial decontamination is achieved by high temperature Er:YAG irradiation.
- Stimulation of reparative processes: treatment with the SMA module based on acousto-interferential cell microtraumatising mechanism which produces effective resonance to achieve tissue regeneration.
OUR MAIN ADVANTAGES
- Out-patient treatment
- Immediate pain relief
- Rapid epithelialisation and granulation of wounds
- No risk of infection due to elimination of infectious bacteria and rapid epithelialisation
- Antibiotics are not used
- Any types of wounds are curable
- The technology is a mono-method of laser impact (no use of creams, ointments or lotions required)
HOW RECOSMA WORKS
An Er:YAG laser emission well absorbed by water is used for practical implementation, which is spatially-modulated with the help of the SMA module. As a result, the laser emission hits the tissue surface not in the form of a continuous wide spot, but as an ordered set of micro-spots 50 microns in diameter and density of up to 10 000 per cm2. The distance between micro-spots is also 50 microns.
The nuance which allows us to obtain the desired result lies in the fact that the laser emission is completely absorbed in the most superficial layer of the tissue. In this case there's no wound surface which significantly reduces the risk of infection. We have a cell structure with insignificant micro-ablation, and the effect rendered upon the deep tissue layers is of a non-thermal nature. This way an ordered structure of destroyed cells is created, surrounded by functioning non-traumatised cells, and since the destroyed cells do not pose a threat to the non-traumatised cells, the fibrosis mechanism isn't triggered.
In response to cell destruction, all reparative processes are activated. Lipolytic enzymes, neutrophils, macrophages, fibroblasts and mast cells are activated. On the fifth day after exposure, there's a noticeable strengthening of skin vascularisation.
Between capillaries there are fibroblasts which activate the synthesis of intercellular substances (collagen, elastic fibres, primary substances) and enable the regeneration of dermis sections subject to alteration. 10 days after exposure the structural-functional organisation of the damaged part of the skin is completely rejuvenated. Collagen and elastic fibres are restored, and a multitude of connective tissue, fibroblasts and macrophages are detected.
This way, during such exposure partial cell destruction occurs, leading to the growth of young fully functional tissue without the onset of fibrosis.
The strength of the acoustic waves is adjusted so that they are insufficient for the independent destruction of cell structures. Degradation only occurs at those places where the fronts of several waves meet.
By changing the energy and pulse duration we can vary the strength of these waves and thus change the depth and degree of micro-traumatisation. Data of histological research confirms the maximal impact depth up to 6 mm.
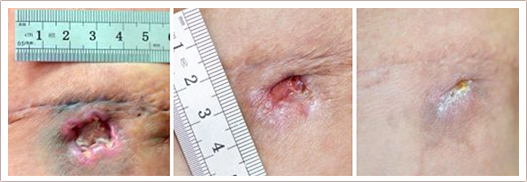
Vascular & Leg vein treatment
The treatment of angiodysplasia, telangiectasia and varicose veins is a serious problem as the currently used methods (cryodestruction, sclerotherapy, surgical excision, and classic laser percutaneous coagulation) are not effective enough and have an increased risk of complications. Our methods can be used to treat a variety of vascular diseases with a high degree of selectivity, allowing us to conduct coagulation sessions without anesthesia, burns and scarring.
Endovasal laser coagulation of varicose veins is actively used in various clinics around the world and is a good alternative to the classic phlebextraction, allowing you to significantly shorten the rehabilitation period. However, laser impact parameters currently used in most clinics are not ideal. Thanks to the optimization of the spectral, energy and time parameters of laser radiation, we have been able to reduce the radiation dose needed for the vein coagulation 2-3 times. This results in much lower thermal damage to adjacent tissue and a shorter rehabilitation period.
Percutaneous laser coagulation is an alternative to the sclerotherapy of varicose veins (telangiectasia), especially in cases where the small vein size does not permit the insertion of a needle. This method has been known for more than thirty years, but laser devices used for phlebology in most cases do not provide a truly selective impact. The lack of impact selectivity unnecessarily increases the percentage of complications in the form of burns with the subsequent growth of fibrous tissue. Our original method has an increased degree of selectivity allowing the coagulation of varicose veins without burns and without scarring the skin.
Percutaneous coagulation using the MULTILINE™ device can be particularly demonstrated in the treatment of progressing haemangiomas in infants during the first year of life. Haemangiomas are destroyed without the formation of an aesthetic defect that cannot be achieved using either conservative methods such as cryodestruction, or surgery (excision), or even using classical vascular lasers and photosystems.